There are a variety of ways in which the exchanges quote security prices to the public. These levels vary by the amount of information and access they provide to investors and traders, and the data typically comes from the exchange that offers the market.
Level I
Level I quotes provide the most basic level of market information. They consist of real-time bid/ask quotes for securities trading on the exchanges and other over-the-counter markets, plus the price at which the most recent trade was executed. Level I access doesn’t disclose the market makers who are bidding for or offering the security, whether there are any limit orders on the security or the size of the potential trades at each price level. As a result, you can’t see the depth of the order book, and you can’t see who is interested in trading and at what price. While Level I quotes may suffice for many investors, active traders need access to the complete order book and market depth that Level II offers.
Level II
Level II is essentially the order book for securities, which means you can see all the available prices and order sizes the market makers and ECNs are posting – plus who’s doing the posting. The information is typically displayed as a table, where bid prices and sizes appear on the left-hand columns of the table and ask prices and sizes are on the right-hand columns.
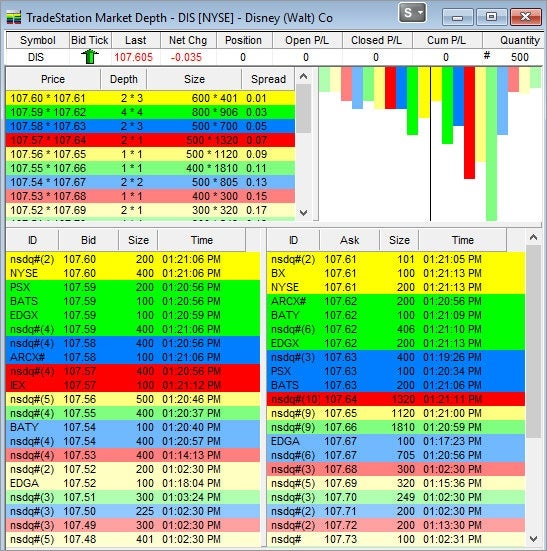
Level II quotes for MSFT. Image courtesy TradeStation.
While Level I shows only the inside or best bid and ask prices, Level II displays the supply and demand of the price levels on either side of the national best bid offer (NBBO) price. This provides a visual display of the current price range and liquidity at each price level – which can be useful when determining trade entry and exit points. It’s important to note that Level II quotes don’t represent actual trades that have happened; they just show how much interest there may be, and at what price. Keep in mind that high-frequency trading programs may adjust Level II bid and ask prices to “shake the tree” and scare onlookers.
While it used to be difficult for individual investors and traders to access Level II quotes, many brokerage firms now offer them as optional data subscriptions. If you meet minimum account requirements, you may receive Level II access for free, depending on your broker. (For related reading, see Introduction to Level II Quotes.)
Level III
Level III quotes are the highest level of quotes provided by a trading service. They include everything in Level II plus the ability to enter quotes, execute orders and send information. Retail investors and traders generally don’t have access to the information; this service is restricted to NASD member firms that function as registered market makers. Level III allows you to enter bid/ask quotes as the trades are being executed right in front of you. It is the fastest way to execute a trade and is typically found only on the trading floors of brokerage firms and market makers.
Electronic Trading: Conclusion
-
 Personal Finance
Personal FinanceWhat To Expect On The CFA Level II Exam
Learn about the nuances of the CFA Level II exam, which goes more in-depth into investment management and portfolio concepts. -
 Personal Finance
Personal FinanceTips for Taking the CFA Exam: Part 2
Peter Mackey, head of exam development for the CFA Institute, shares his tips for passing the CFA level I, II and III exams. -
 Trading
TradingHigh-Frequency Trading: A Primer
An in depth look at how high-frequency trading works and who the players are. -
 Trading
TradingThe Basics of the Bid-Ask Spread
The bid-ask spread is the difference between the bid price and ask price prices for a particular security. -
 Personal Finance
Personal FinanceHow brokers can avoid a market-maker's tricks
Ensure that you and your clients are getting the best deal by avoiding these three pitfalls. -
 Trading
TradingECN Credits: Let Your Broker Pay Your Trading Fees
Altering your entry and exit strategy could save you a lot of money in fees. Find out how to pad your bottom line. -
 Financial Advisor
Financial Advisor6 Proven Tips For Series 6 Success
These techniques can help you pass the Series 6 exam without the added stress. Here are six tips to get you ready. -
 Investing
InvestingThe Daily Routine Of A Swing Trader
From pre-market to after hours, see what you need to do to capture gains quickly. -
 Financial Advisor
Financial AdvisorHow Hard are the CFA Exams?
Learn about the difficulty of the CFA exams with a description of the tests, some statistics on pass rates and suggestions that can help you pass the exams.



